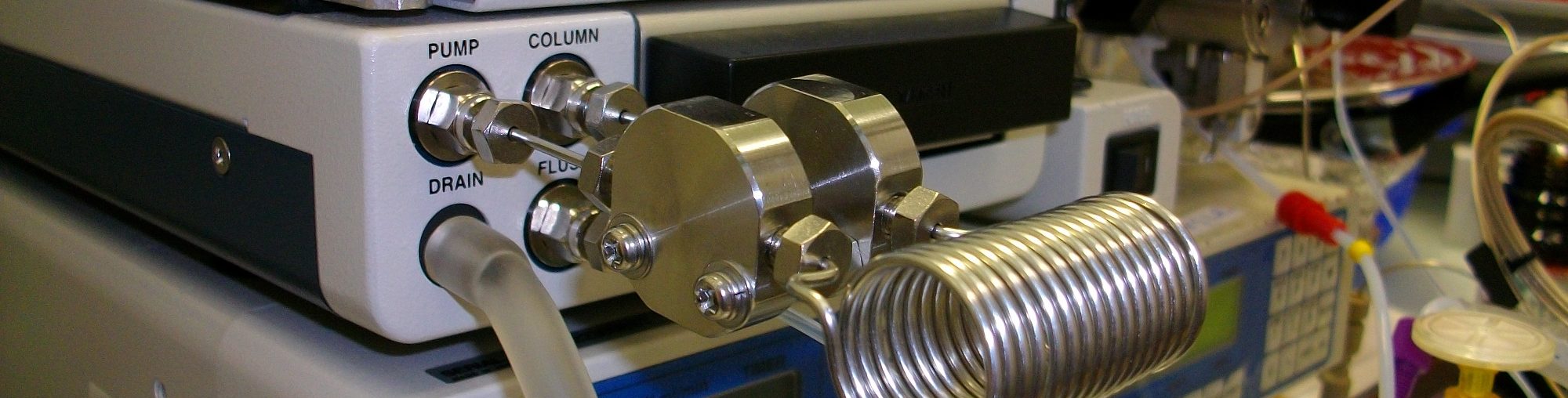
Flow Chemistry
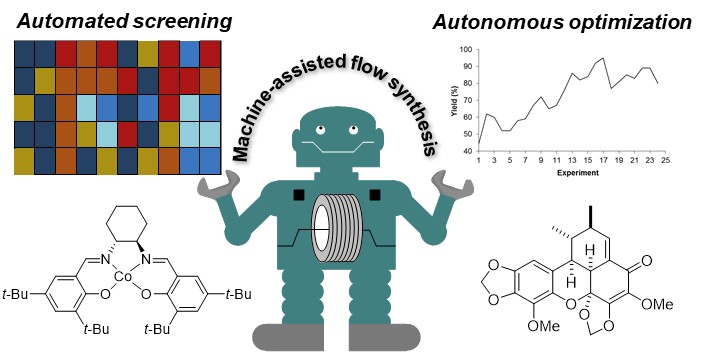
The use of machines and robots to assist chemists in labor-intensive and routine processes will certainly profoundly modify the organization of synthetic laboratories in the next future. While the way to synthesize molecules has not been significantly modified these last 40 years, the situation is changing rapidly owing to the need to develop more sustainable process in a safe working environment.
In this framework, we are developing powerful automated flow-based strategies associating real-time monitoring and process-control instrumentation.
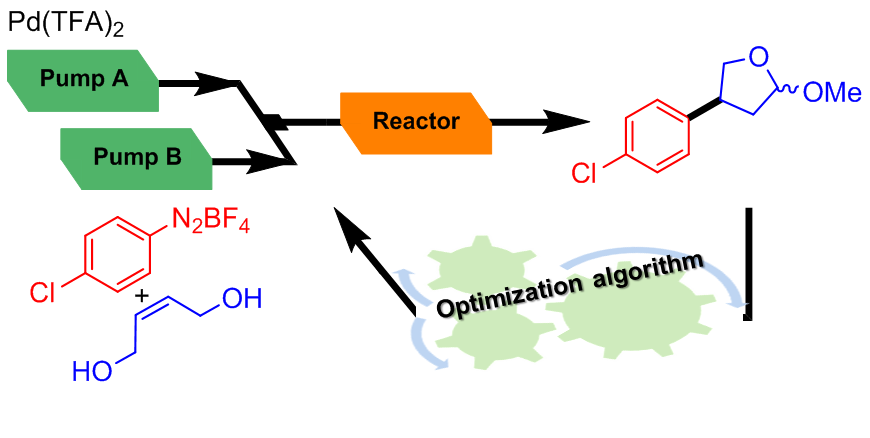
Our machine can be configured as an automated platform for the screening on µmol scale to identify the most promising experimental conditions (catalyst or reagent screening). The automated screening platform can be reconfigurated into an autonomous self-optimizing flow reactor by implementation of an optimization algorithm in the closed-loop system.
Such systems have been used for the handling of hazardous compounds such as arenediazonium salts and for the biomimetic synthesis of natural products.
- Selected key references
Ø Diazonium salts in flow: J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 8255 / Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 590
Ø Flow device with algorithm: Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1979
Ø On-board flow device: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7568
Ø Automated flow device: J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 14286 / React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 1608 / J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 14101-14112
Cellulose
Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer on earth and one of the cheapest sustainable raw material, mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Cellulose is a linear polysaccharide of (1 à 4) linked d-glucose that is very attractive since it is an inexpensive and disposable material having interesting physical and chemical properties like hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, biodegradability, and chemical reactivity through its hydroxyl groups. Paper is one of the oldest use of cellulose that has found numerous applications as support for writing, as packing…
Our objective is to transform the thousand-year-old paper into a high-tech material for many applications including sensing, remediation, catalysis and covalent printing.
- Selected key references
Ø Sensing:Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2525 / Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6569
Ø Remediation:ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1965
Ø Catalysis:Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13549
Ø Covalent printing:Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7672 / J. Mat. Chem. C. 2017, 5, 5154

Chemistry of diazonium salts
Aryl diazonium salts are highly reactive compounds and used as aryl halide surrogates in Pd-catalyzed reactions. The super-electrophile properties of aryl diazonium salts allows reactions to proceed under mild conditions (T<60°C), without the need of ligand, and even sometimes, base. The simple and efficient experimental procedure features many advantages, including energy, cost, and waste benefits that are of interest for the development of sustainable processes.
Aryl diazonium salts are also well-known aryl radical precursors that have been widely used in many transformations including the copper-catalyzed Meerwein arylation. With this picture, one could imagine that aryl diazonium salts are ideal partners for many transformations. Unfortunately, the high nucleofugic properties of the diazonium function, giving nitrogen release, makes these compounds rather unstable and potentially explosive.
Our team develop new methodologies in palladium and copper catalysis allowing the handling of diazonium salts in safer conditions. For instance, we developed a new concept of cooperative catalysis allowing the use of substoichiometric amounts of diazonium salts.

- Selected key references
Ø Palladium catalysis: Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5191 / Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2646 / Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 7210 / Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9291 / Org. Process Res. Dev. 2014, 18, 1786 / Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1065 / ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2085 / New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8855 / ChemCatChem, 2016, 8, 1998
Ø Copper catalysis: Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5236 / Carbon, 2015, 93, 974
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Supporting catalysts on a solid support allows an easy recovery by simple filtration and offers the possibility of recycling expensive metals or organocatalysts. Our studies aim at developing simple and sustainable catalyst systems, using mainly carbon-based material as support or catalysts. We also investigate in depth the often-experienced catalyst deactivation and propose new concepts to address this issue. For instance, we proposed a concept of catalysis by a supported Pd-Au alloy, where Pd act as an active metal, while Au acts as a stabilizing metal for nanoparticles. We also developed the concept of multi-task or multi-functional heterogeneous catalysts. More recently, we also studied the peculiar properties of graphene for biomass transformations under mild conditions.
- Selected key references
Ø Heterogeneous palladium catalysis: Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 33 / Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 14024 / ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2175 / Synlett 2014, 25, 1055 / Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2014, 482, 157
Ø Heterogeneous copper catalysis: Carbon 2015, 93, 974
Ø Heterogeneous multi-functional catalysts: Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 7238 / J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1349 / ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2085
Ø Graphene: Carbon 2016, 96, 342 / Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1531

